Types of Roofs in Building Construction: A Comprehensive Guide

Table of Contents
When it comes to building construction, the roof is an essential component that plays a significant role. The roof protects the building from harsh weather conditions, enhances its aesthetic appeal, and provides insulation to keep the interior comfortable. There are various types of roofs that can be used in building construction, each with its unique features and benefits.
One of the most common types of roofs is the pitched roof, which has a sloping surface and is often seen in residential buildings. The pitch of the roof can vary, and the design can include variations such as gable, hip, gambrel, and mansard roofs. Pitched roofs are known for their durability, versatility, and ability to shed water quickly. Another type of roof is the flat roof, which is commonly used in commercial buildings. Flat roofs are cost-effective, easy to install, and can provide additional space for equipment or storage. However, they require regular maintenance to prevent water pooling and leaks. when hiring a civil construction company, you should talk to their professionals about all the possible construction details as it may help you ensure that you hire the right contractor.
Historical Evolution of Roofing

Roofing has been an integral part of building construction for centuries. The evolution of roofing materials and techniques throughout history reflects humanity’s ingenuity, adaptability, and pursuit of innovation. From ancient civilizations’ primitive thatch roofs to modern-day sustainable roofing solutions, the roofing industry has continuously evolved to meet the changing needs and demands of society.
In ancient times, people used natural materials such as straw, leaves, and branches to construct roofs. These materials were readily available and provided basic protection from the elements. Over time, people began to use more durable materials such as clay and stone tiles, which could withstand harsh weather conditions and last longer.
During the Middle Ages, the use of thatch roofs became popular in Europe. Thatch roofs were made of straw, reeds, or other natural materials that were woven together and laid over a wooden frame. Thatch roofs provided excellent insulation and were relatively cheap to construct. However, they were also highly flammable and required regular maintenance to prevent rotting and damage from insects.
In the 19th century, the Industrial Revolution brought about significant changes in the roofing industry. The development of new materials such as asphalt and metal allowed for more durable and long-lasting roofs. The use of slate and tile roofs also became more prevalent during this time, as they provided a more elegant and sophisticated look to buildings.
In the modern era, roofing technology has continued to advance rapidly. Today, there are a wide variety of roofing materials and techniques available, including green roofs, solar roofs, and reflective roofs. These innovative solutions provide increased energy efficiency, reduced environmental impact, and improved durability.
Overall, the historical evolution of roofing reflects the changing needs and demands of society over time. As technology continues to advance, the roofing industry will likely continue to evolve and adapt to meet the needs of future generations.
Basic Roof Design Principles
The design of a roof is an essential aspect of building construction. It not only serves as a protective covering but also plays a significant role in the overall aesthetics of the building. Here are some basic roof design principles that are essential to consider when designing a roof:
1. Roof Pitch
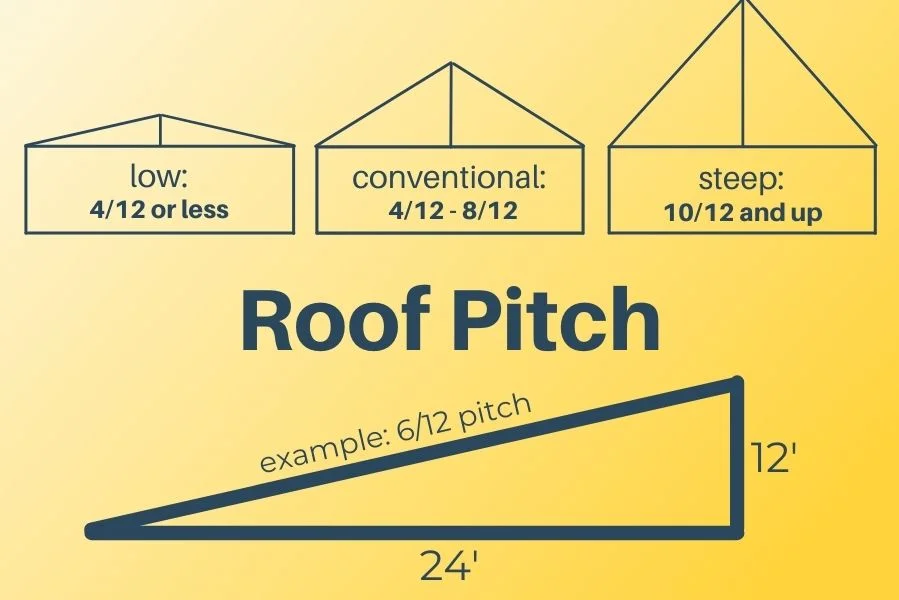
Roof pitch is the angle at which the roof slopes. It is an essential factor in determining the type of roof that is suitable for a building. The pitch of a roof affects its ability to shed water, snow, and debris. A steeply pitched roof is suitable for areas with heavy snowfall, while a flat or low-pitched roof is suitable for areas with low rainfall.
2. Roof Shape
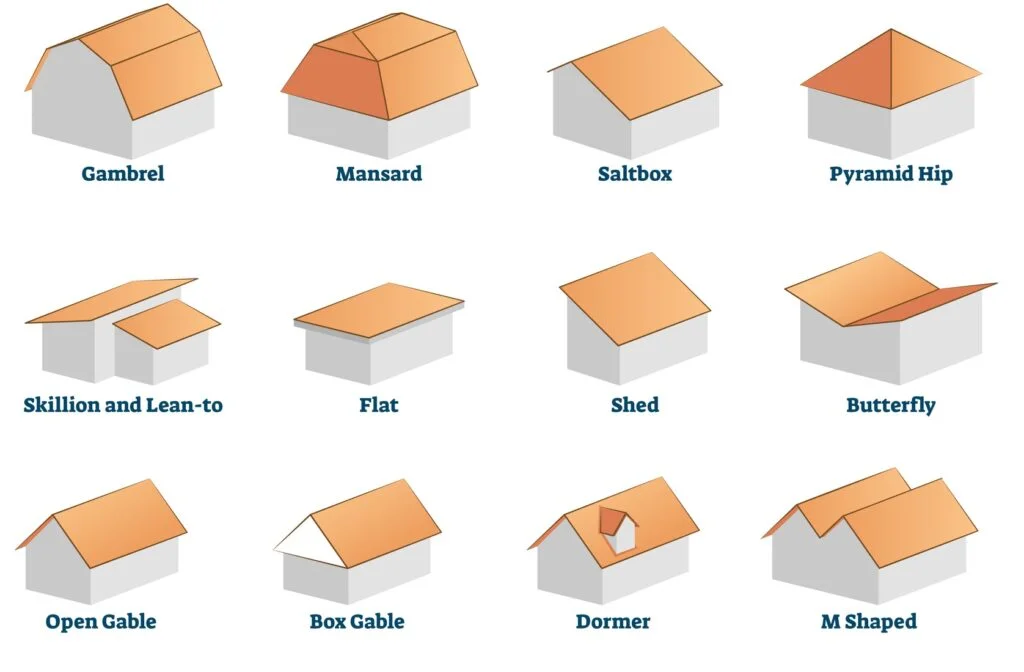
The shape of a roof also plays a crucial role in the overall design of a building. The most common roof shapes are flat, gable, hip, and mansard. The choice of roof shape depends on the architectural style of the building, the climate, and the building’s purpose.
3. Roof Materials
The choice of roofing materials is another critical aspect of roof design. The most common roofing materials include asphalt shingles, metal, clay tiles, and concrete tiles. The choice of roofing material depends on several factors, including durability, cost, and aesthetic appeal.
4. Roof Ventilation
Proper roof ventilation is essential to prevent moisture build-up, which can lead to mold growth and other structural issues. A well-ventilated roof also helps to regulate the temperature inside the building, reducing the load on the HVAC system.
5. Roof Load
The roof load is the weight that the roof can support without collapsing. The roof load depends on several factors, including the type of roofing material, the pitch of the roof, and the building’s location. It is essential to ensure that the roof load is adequate to prevent structural damage and ensure the safety of the occupants.
In conclusion, the design of a roof is a critical aspect of building construction. The roof pitch, shape, materials, ventilation, and load are essential factors that must be considered when designing a roof. By following these basic roof design principles, builders can ensure that the roof is not only functional but also aesthetically pleasing.
Types of Roofing Materials
When it comes to roofing materials, there are a variety of options available to builders and homeowners. Each type of roofing material has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of material will depend on factors such as budget, climate, and personal preference.
1. Asphalt Shingles
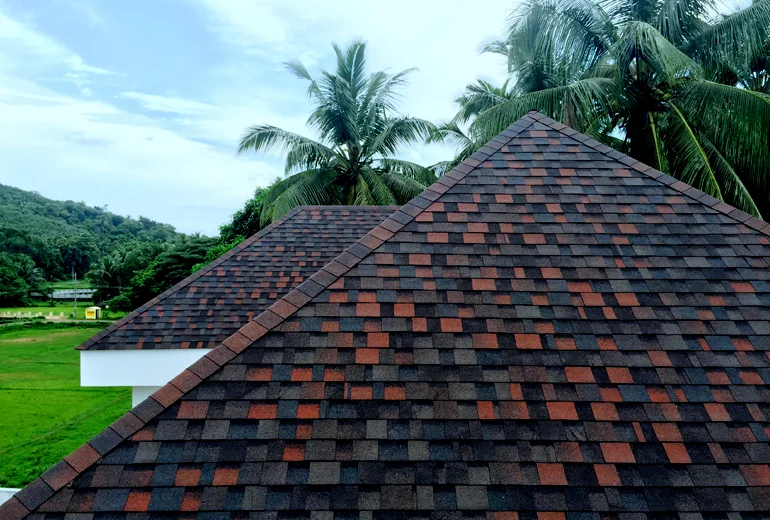

Asphalt shingles are one of the most popular roofing materials. They are affordable, easy to install, and come in a variety of colors and styles. Asphalt shingles are made from a fiberglass mat that is coated with asphalt and covered with mineral granules. They are durable and can last up to 20-30 years with proper maintenance. You can learn more about asphalt shingle roofs here.
2. Metal Roofing
Metal roofing is a durable and long-lasting option for homeowners. It is available in a variety of materials, including aluminum, steel, and copper. Metal roofs are energy-efficient and can help reduce energy costs. They are also fire-resistant and can withstand harsh weather conditions.
3. Wooden Shakes and Shingles
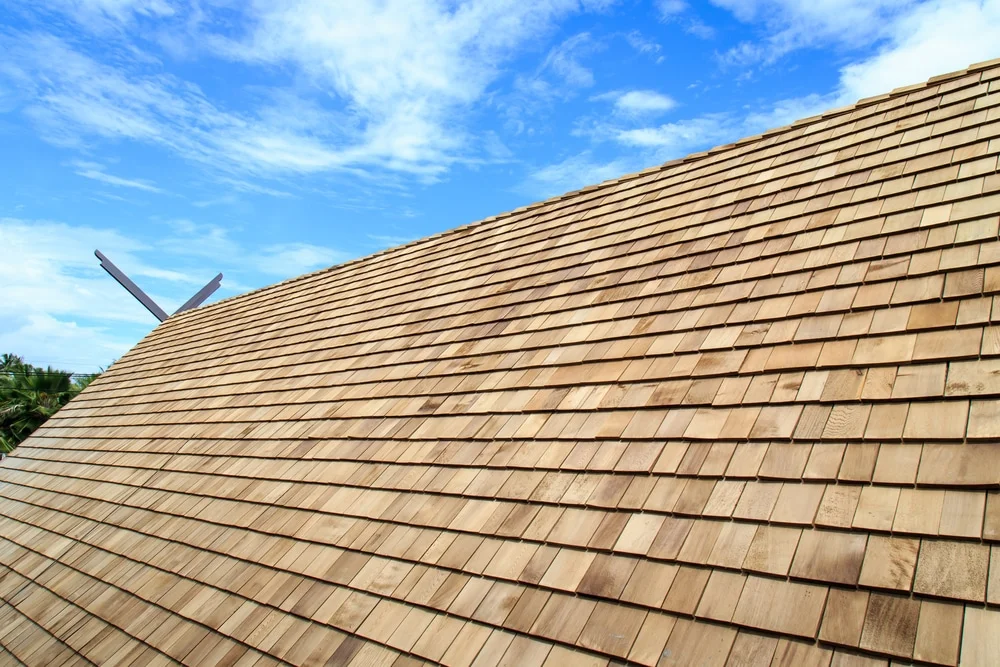

Wooden shakes and shingles are traditional roofing materials that can add a rustic look to a home. They are made from cedar, redwood, or other types of wood and are environmentally friendly. Wooden roofs require regular maintenance to prevent rot and decay and can be expensive to install.
4. Clay and Concrete Tiles
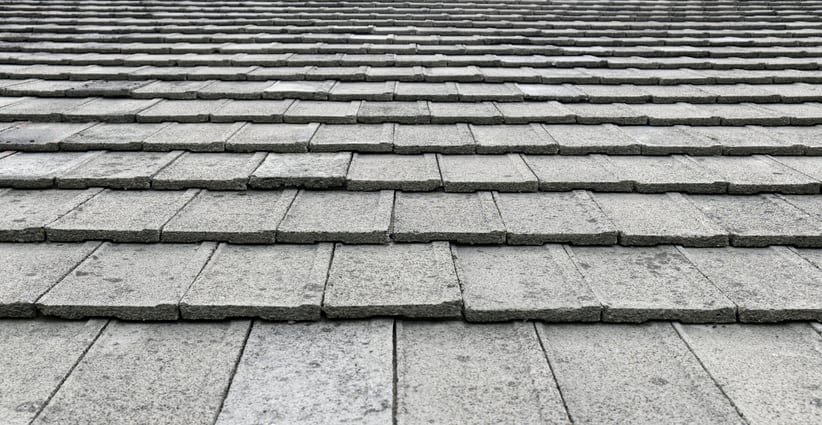

Clay and concrete tiles are a popular choice for homeowners who want a durable and long-lasting roof. They are available in a variety of colours and styles and can be designed to mimic the look of other roofing materials such as wood or slate. Clay and concrete tiles are heavy and require a strong support structure.
5. Slate Roofing

Slate roofing is a high-end roofing material that is known for its durability and longevity. It is made from natural stone and can last up to 100 years. Slate roofing is also fire-resistant and can withstand harsh weather conditions. However, it is expensive to install and requires a strong support structure.
6. Synthetic Roofing Products

Synthetic roofing products are a newer option for homeowners. They are made from a variety of materials such as rubber, plastic, and polymer. Synthetic roofs can mimic the look of other roofing materials and are lightweight and easy to install. They are also durable and can last up to 50 years with proper maintenance.
Overall, the choice of roofing material will depend on a variety of factors such as budget, climate, and personal preference. Homeowners should consider the pros and cons of each type of roofing material before making a decision.
Roof Shapes and Styles
When it comes to building construction, roofs come in many shapes and styles. Each type has its unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of the roof shape and style depends on various factors such as climate, architectural design, and budget.
1. Gable Roofs

Gable roofs are the most common type of roof shape in residential construction. They are also known as pitched or peaked roofs. Gable roofs have two sloping sides that meet at the ridge or the highest point of the roof. The sides of the gable roof can be of equal length or different lengths, depending on the design. Gable roofs are easy to construct, provide ample space for an attic or a vaulted ceiling, and are excellent for shedding water and snow. However, they can be problematic in areas with high winds or hurricanes.
2. Hip Roofs
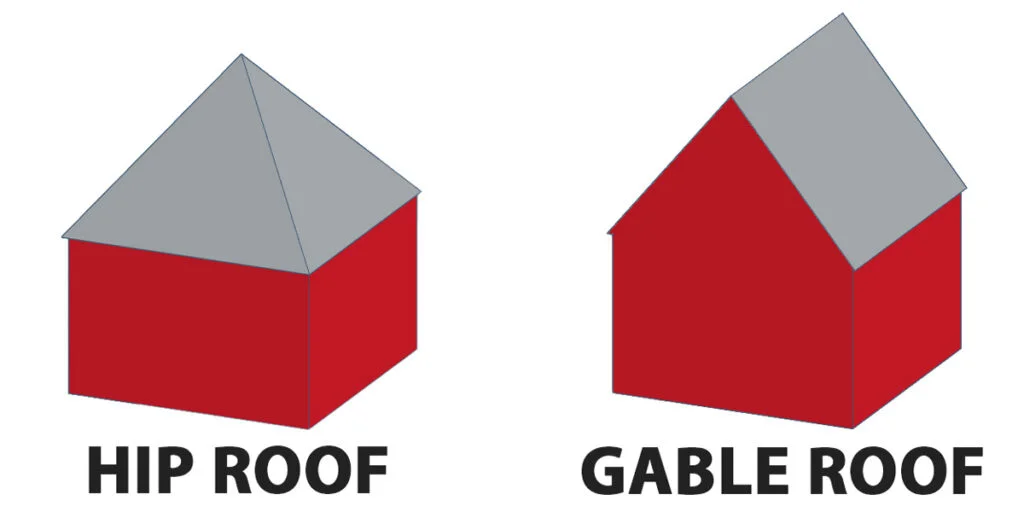
Hip roofs are also a common type of roof shape in residential and commercial construction. They have four sloping sides that meet at the ridge, forming a pyramid-like shape. Hip roofs are more stable than gable roofs in high winds and provide better protection against hurricanes. They also provide more shade and ventilation and are suitable for areas with hot climates. However, hip roofs are more complex to construct than gable roofs, and the additional seams can make them more prone to leaks.
3. Flat Roofs
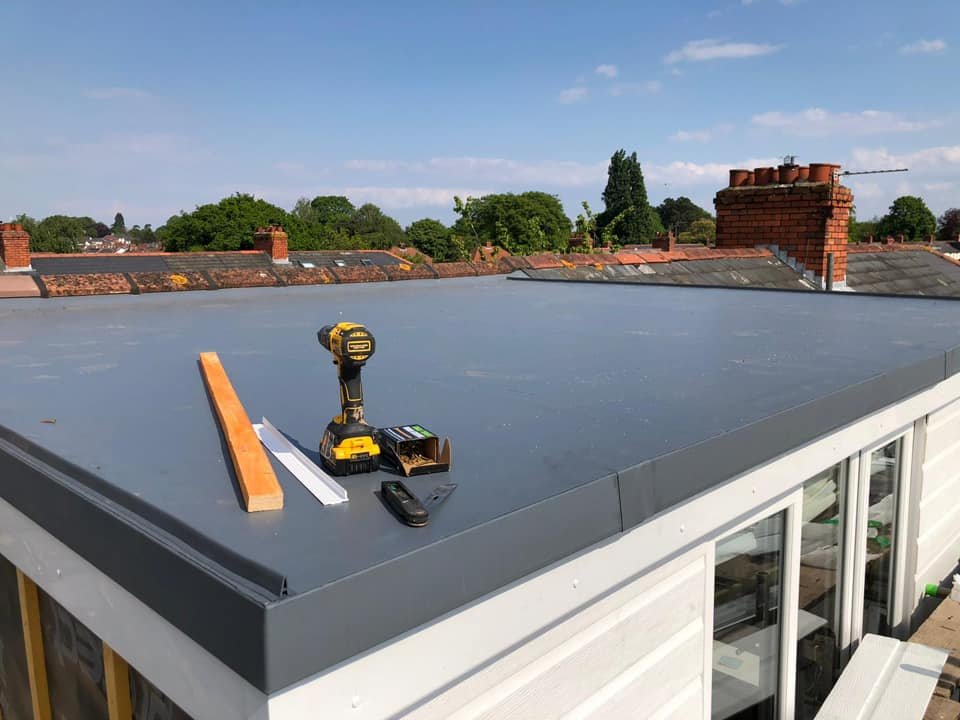

Flat roofs are a popular choice for commercial and industrial buildings. They are also used in some residential construction, particularly in modern and contemporary designs. Flat roofs are easy to construct, provide additional outdoor living space, and are cost-effective. However, flat roofs require regular maintenance, are prone to leaks, and may not be suitable for areas with heavy snow or rain.
4. Mansard Roofs

Mansard roofs, also known as French roofs, are a popular choice for historic and traditional buildings. They have four sloping sides, with the lower slope steeper than the upper slope. Mansard roofs provide additional living space, particularly in the attic, and are suitable for areas with high snowfall. However, mansard roofs are more expensive to construct than other types of roofs and require regular maintenance.
5. Gambrel Roofs
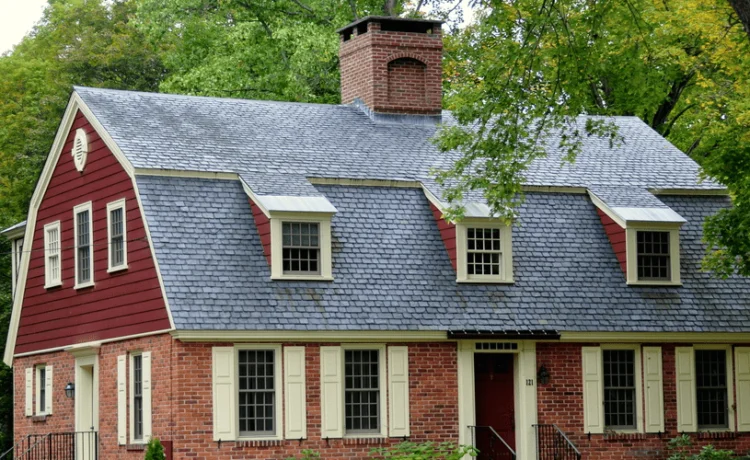

Gambrel roofs are a type of roof shape that resembles a barn roof. They have two sloping sides on each of the two roof planes, with the lower slope steeper than the upper slope. Gambrel roofs provide additional living space, particularly in the attic, and are suitable for areas with high snowfall. However, gambrel roofs are more complex to construct than other types of roofs and may require additional reinforcement.
6. Shed Roofs

Shed roofs are a simple and cost-effective type of roof shape. They have one sloping side and are commonly used in sheds, garages, and other small structures. Shed roofs are easy to construct and provide good drainage. However, shed roofs are not suitable for areas with heavy snow or rain, and they provide limited living space.
7. Butterfly Roofs
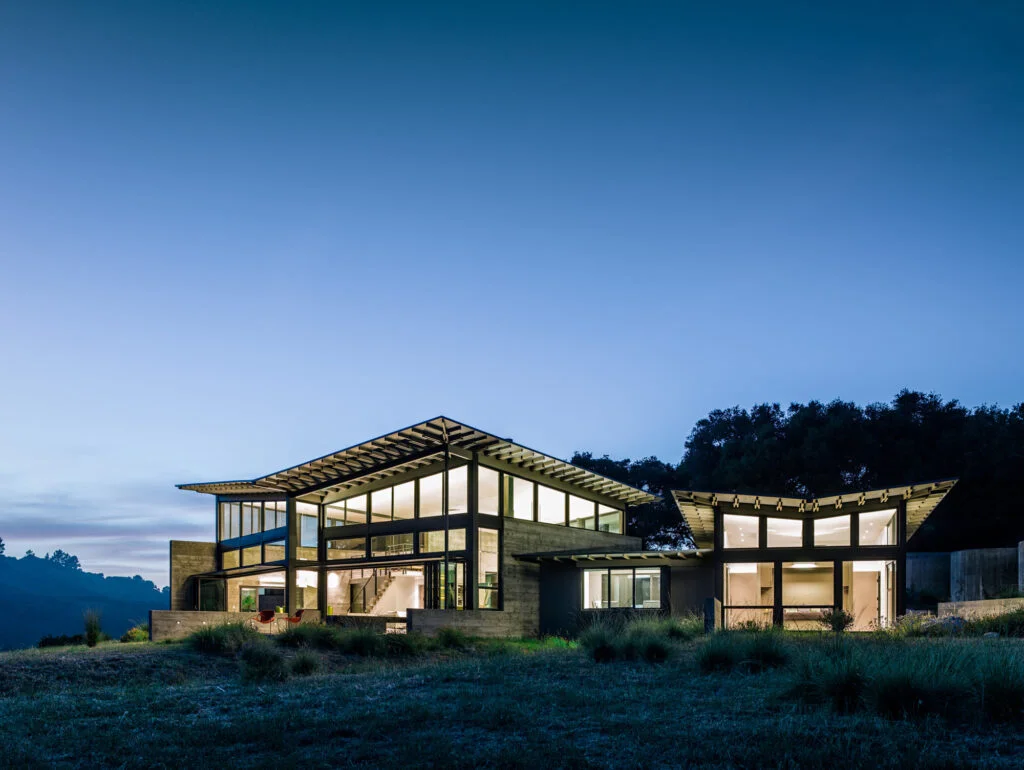

Butterfly roofs are a modern and unique type of roof shape. They have two sloping sides that meet at the center, forming a V-shape. Butterfly roofs provide ample natural light, ventilation, and outdoor living space. However, butterfly roofs are more complex to construct than other types of roofs and may require additional insulation.
8. Dome Roofs

Dome roofs are a rare and unique type of roof shape. They have a curved or spherical shape and are commonly used in religious and cultural buildings. Dome roofs provide excellent structural support, natural light, and ventilation. However, dome roofs are more complex to construct than other types of roofs and require specialized skills and materials.
Roofing System Components
When it comes to building construction, roofing systems play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and longevity of a structure. A roofing system comprises several components that work together to provide protection against the elements, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the aesthetics of a building.
1. Underlayment
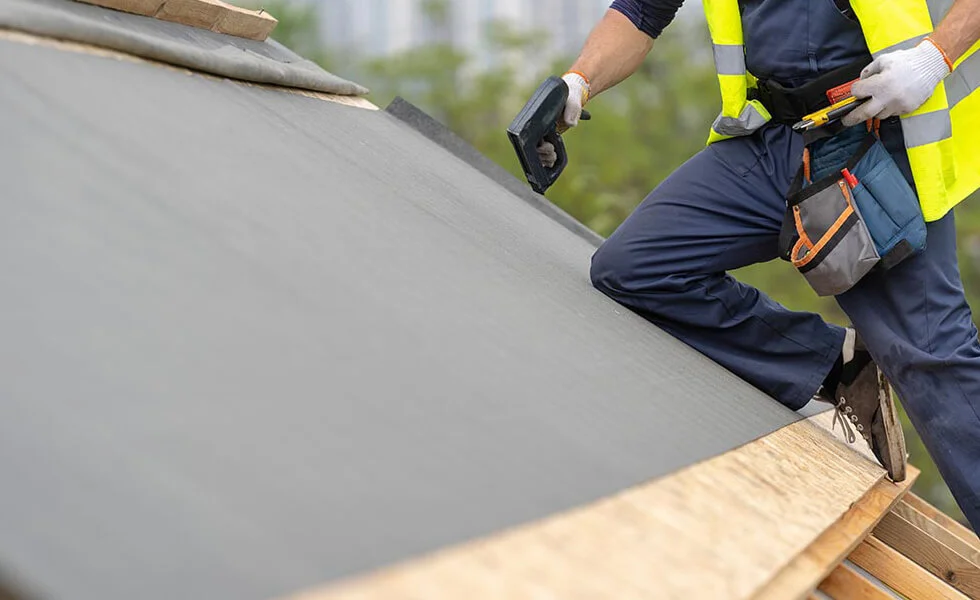

Underlayment is a thin layer of material that is installed between the roof covering and the roof deck. Its primary function is to provide an additional layer of protection against water infiltration, wind-driven rain, and other weather-related elements. It also helps to improve the energy efficiency of a building by reducing heat loss and heat gain. You can learn more about how underlayment helps protect your home here.
2. Flashing

Flashing is a thin strip of material that is installed around roof penetrations, such as chimneys, skylights, and vents, to prevent water from seeping in. It is typically made of metal, such as copper, aluminum, or galvanized steel, and is designed to be durable and long-lasting.
3. Gutters and Downspouts
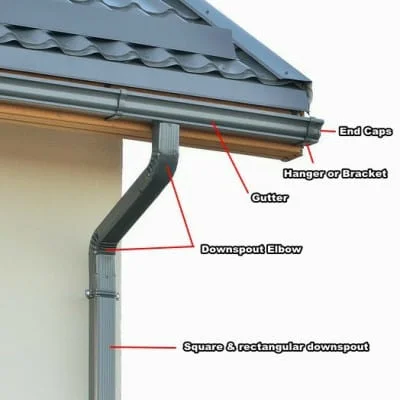

Gutters and downspouts are an essential part of any roofing system, as they help to collect and channel rainwater away from the building’s foundation. Gutters are typically made of metal or vinyl and are installed along the roofline to collect rainwater. Downspouts are connected to the gutters and are used to direct the water away from the building.
4. Ventilation Features
Ventilation features are crucial to the overall performance and longevity of a roofing system. They help to regulate the temperature and moisture levels in the attic, which can prevent damage to the roof deck, shingles, and other components. Some common ventilation features include ridge vents, soffit vents, and gable vents.
In summary, a roofing system comprises several components that work together to provide protection against the elements, improve energy efficiency, and enhance the aesthetics of a building. Underlayment, flashing, gutters and downspouts, and ventilation features are just a few of the essential components that are required to ensure a functional and durable roof.
Sustainability and Green Roofing Options

In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards sustainable building practices. One area where this has been particularly evident is in the use of green roofing options. Green roofs, also known as living roofs, are roofs that are covered in vegetation. They offer a range of benefits, including improved insulation, reduced energy costs, and improved air quality.
There are several types of green roofs, including extensive, semi-intensive, and intensive. Extensive green roofs are the most common type and are typically used on commercial buildings. They are lightweight and require minimal maintenance, making them an ideal option for buildings with limited roof access. Semi-intensive green roofs are slightly more complex and require more maintenance than extensive green roofs. They are often used on residential buildings and can support a wider range of vegetation. Intensive green roofs are the most complex and require the most maintenance. They are typically used on larger buildings and can support a wide range of vegetation, including trees and shrubs.
Another sustainable roofing option is cool roofs. Cool roofs are designed to reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat than traditional roofs. This can help to reduce the amount of energy required to cool a building, which can result in significant cost savings over time. Cool roofs are available in a range of materials, including asphalt, metal, and tiles.
In addition to green and cool roofs, there are several other sustainable roofing options available. These include rubberized roofs, which are made from recycled tires, and clay tile roofs, which are made from natural materials and can last for up to 100 years with proper maintenance. Solar tile roofs are another option, which can help to reduce energy costs by generating electricity from the sun.
Overall, there are several sustainable roofing options available for building construction. Green roofs, cool roofs, and other sustainable options can help to reduce energy costs, improve air quality, and promote sustainable building practices.
Roof Insulation and Energy Efficiency

Roofing for Different Climates
Roof insulation is an essential component of any building construction, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining the indoor temperature and reducing energy consumption. Insulated roofs are more energy-efficient than uninsulated ones, as they prevent heat transfer between the interior and exterior of the building.
The type of insulation used in a roof depends on the climate, building design, and budget. According to a study published in the Journal of Building Engineering, vaulted and domed roofs are the most efficient roof forms in hot and dry climates (without any insulation). However, in other climates, insulators such as polyurethane, Rockwool, air, and water can be used to achieve the desired level of thermal insulation. The lowest U-value can be achieved by corrugated fibrous cement with 50 mm PUF.
When it comes to roofing, one size does not fit all. The choice of roofing material should be based on the climate of the area where the building is located. Different types of roofing materials have different characteristics that make them suitable for different climates.
In hot climates, it is important to choose a roofing material that reflects sunlight and heat. This helps to keep the building cool and reduces the amount of energy required to cool the building. Materials such as metal, tile, and asphalt shingles are good choices for hot climates. Metal roofs, in particular, are highly reflective and can reduce the amount of heat absorbed by the building.
In cold climates, it is important to choose a roofing material that can withstand heavy snow loads and extreme temperatures. Materials such as slate, tile, and metal are good choices for cold climates. These materials are durable and can withstand the weight of heavy snow loads.
In areas with high winds, it is important to choose a roofing material that can withstand strong winds. Materials such as metal, asphalt shingles, and tile are good choices for windy areas. Metal roofs, in particular, are highly resistant to wind damage.
In areas with heavy rainfall, it is important to choose a roofing material that can withstand moisture and prevent leaks. Materials such as asphalt shingles, metal, and tile are good choices for areas with heavy rainfall. These materials are durable and can prevent water from entering the building.
In areas with extreme weather conditions, it may be necessary to choose a roofing material that can withstand multiple weather conditions. Materials such as metal, tile, and slate are good choices for areas with extreme weather conditions. These materials are durable and can withstand a wide range of weather conditions.
In summary, the choice of roofing material should be based on the climate of the area where the building is located. Different types of roofing materials have different characteristics that make them suitable for different climates. By choosing the right roofing material, building owners can ensure that their building is protected from the elements and remains in good condition for many years to come.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations

When it comes to building construction, choosing the right type of roof is crucial to ensure the longevity and durability of the structure. However, it is equally important to maintain the roof regularly to keep it in good condition and prevent any potential damage.
Different types of roofs require different levels of maintenance. For instance, flat roofs require more frequent maintenance than sloped roofs as they tend to accumulate water, debris, and other materials that can cause damage over time. Regular inspections, cleaning, and repairs should be carried out to prevent any potential leaks or damage to the roofing material.
Another important consideration for roof maintenance is the choice of roofing material. Some materials, such as metal and tile, are more durable and long-lasting than others, such as asphalt shingles. However, they may also require more maintenance and repairs to keep them in good condition. It is important to choose a roofing material that is appropriate for the climate and weather conditions in the area, as well as the specific needs and requirements of the building.
In addition to regular maintenance, there are also several measures that can be taken to improve the durability and longevity of a roof. These include proper installation, adequate ventilation, and the use of high-quality materials. By taking these steps, building owners can ensure that their roofs are able to withstand the elements and last for many years to come.
Innovations in Roofing Technology
The roofing industry has undergone significant changes in recent years, thanks to advancements in technology. These innovations have brought about more efficient, durable, and sustainable roofing solutions that cater to the needs of modern homeowners. In this section, we will discuss some of the most prominent innovations in roofing technology.
1. Cool and Smart Roofing Systems

Cool roofs are designed to reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat, making them an ideal solution for hot climates. They are coated with a highly reflective type of paint, a sheet covering, or highly reflective tiles or shingles. Smart roofs, on the other hand, use sensors and other technologies to monitor and adjust the temperature of the roof based on the weather conditions. This helps to reduce energy costs and increase the lifespan of the roof.
2. Robotics
Robotics is another area where the roofing industry has seen significant advancements. Robotic shingle installers are gaining popularity due to their efficiency, safety, and accuracy. These robots are winch-based and require minimal human intervention to operate. They can reload shingles automatically, reducing the need for manual labor and increasing the speed of installation.
3. Sustainable Materials
Sustainability is a growing concern in the construction industry, and the roofing industry is no exception. Innovations in roofing technology have led to the development of sustainable roofing materials such as solar shingles, which generate electricity from the sun, reducing the need for external power sources. Other sustainable materials include recycled rubber, which is used to create durable and long-lasting roofing materials.
4. Drones
Drones are becoming increasingly popular in the roofing industry due to their ability to provide detailed aerial images of the roof. This helps to identify any potential issues, such as leaks or damage and enables contractors to make informed decisions about repairs or replacements. Drones are also used to inspect roofs in hard-to-reach areas, reducing the need for manual labor and improving safety.
In conclusion, innovations in roofing technology have revolutionized the roofing industry, providing homeowners with more efficient, durable, and sustainable roofing solutions. From cool and smart roofing systems to robotics, sustainable materials, and drones, these innovations have made roofing safer, faster, and more cost-effective.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the different architectural styles of roofing in residential construction?
Residential roofing styles can vary greatly depending on the region and architectural style of the building. Some common styles include gable, hip, mansard, and gambrel roofs. Gable roofs are the most common and have a triangular shape. Hip roofs have slopes on all four sides, while mansard roofs have a flat top and steep sides. Gambrel roofs are similar to mansard roofs but have two slopes on each side instead of one.
2. How do various roofing materials impact the longevity and durability of a roof?
The choice of roofing material can greatly impact the longevity and durability of a roof. Some materials, such as metal and concrete, are more durable and long-lasting than others, such as asphalt shingles. However, the durability of a roof also depends on factors such as proper installation, maintenance, and the climate in which the building is located.
3. Can you list the most energy-efficient types of roofing for buildings?
Some of the most energy-efficient types of roofing materials include cool roofs, green roofs, and solar roofs. Cool roofs are designed to reflect sunlight and reduce heat absorption, while green roofs are covered in vegetation that helps regulate temperature and improve air quality. Solar roofs are covered in photovoltaic cells that generate electricity from sunlight.
4. What are the structural differences between flat and pitched roofs in construction?
Flat roofs are horizontal or nearly horizontal, while pitched roofs have sloping sides. Pitched roofs are generally more structurally sound than flat roofs and are better suited for areas with heavy snow or rainfall. Flat roofs, on the other hand, are easier to install and maintain and are often used in commercial buildings.
5. What roofing types are best suited for extreme weather conditions?
The best roofing types for extreme weather conditions depend on the specific weather patterns in the area. For example, metal roofs are often used in areas with high winds and heavy rain, while clay tiles are better suited for areas with high heat and sunlight. It is important to consult with a roofing professional to determine the best roofing material for a specific location.
6. How does the choice of roof design affect the overall aesthetics of a building?
The choice of roof design can greatly impact the overall aesthetics of a building. Different roof styles can complement or contrast with the architectural style of the building and can convey a certain mood or tone. For example, a gable roof can give a building a traditional and classic look, while a flat roof can give a building a modern and minimalist feel.






