Types Of Foundation in Construction You Should Know About

Table of Contents
When it comes to constructing a building, the foundation is the most crucial aspect that needs to be taken into consideration. The foundation of a building provides support and stability to the entire structure. There are different types of foundations in construction, and each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. The type of building getting constructed also plays an important role in deciding which type of foundation to move ahead with.
The type of foundation used in a building construction project depends on various factors such as soil conditions, load capacity, and design. The foundation needs to be designed in such a way that it can withstand the weight of the building and the forces acting upon it. Different types of foundations are used based on the soil type, building size, and environmental conditions. It is important to choose the right type of foundation to ensure the safety and stability of the building. Also, it is highly advisable to have access to a pool of experts with in-depth knowledge of various types of foundations and their practical applications just like we have at Dhinwa Construction.
In this article, we will discuss the different types of foundations used in building construction. We will explore the suitability, advantages, and disadvantages of each type of foundation based on soil conditions, load capacity, and design. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the different types of foundation and their uses in building construction. Having constructed various flats in Jaipur and beyond, which are basically high-rise buildings, let’s dig straight into the fundamentals of foundations.
Foundation Fundamentals
1. Purpose of Foundations

Foundations are an essential component of any building structure. They serve as the base on which the entire weight of the building rests. The primary purpose of a foundation is to transfer the load of the building to the ground in a safe and stable manner. A good foundation ensures that the building remains stable and does not sink or collapse due to the weight of the structure or external factors such as weather conditions or natural disasters.
2. Factors Influencing Foundation Selection
Several factors influence the selection of a foundation for a building. The type of foundation chosen depends on the soil conditions, the size and weight of the building, and the environmental conditions of the area. The following factors are considered while selecting a foundation:
- Soil Type: The type of soil on which the building is to be constructed plays a crucial role in determining the type of foundation required. Different soil types have varying load-bearing capacities, which affects the stability of the building.
- Building Size and Weight: The size and weight of the building determine the depth and width of the foundation required. A larger and heavier building requires a deeper and wider foundation to ensure stability.
- Environmental Conditions: The environmental conditions of the area, such as seismic activity and wind loads, also play a crucial role in determining the type of foundation required. The foundation must be designed to withstand these external factors.
- Cost: The cost of the foundation is also a significant factor in determining the type of foundation required. A shallow foundation is generally less expensive than a deep foundation.
In conclusion, a foundation is an essential component of any building structure. The type of foundation selected depends on various factors such as soil conditions, building size and weight, environmental conditions, and cost. A good foundation ensures that the building remains stable and safe for its occupants.
What are the different types of foundations used in construction?
1. Shallow Foundations
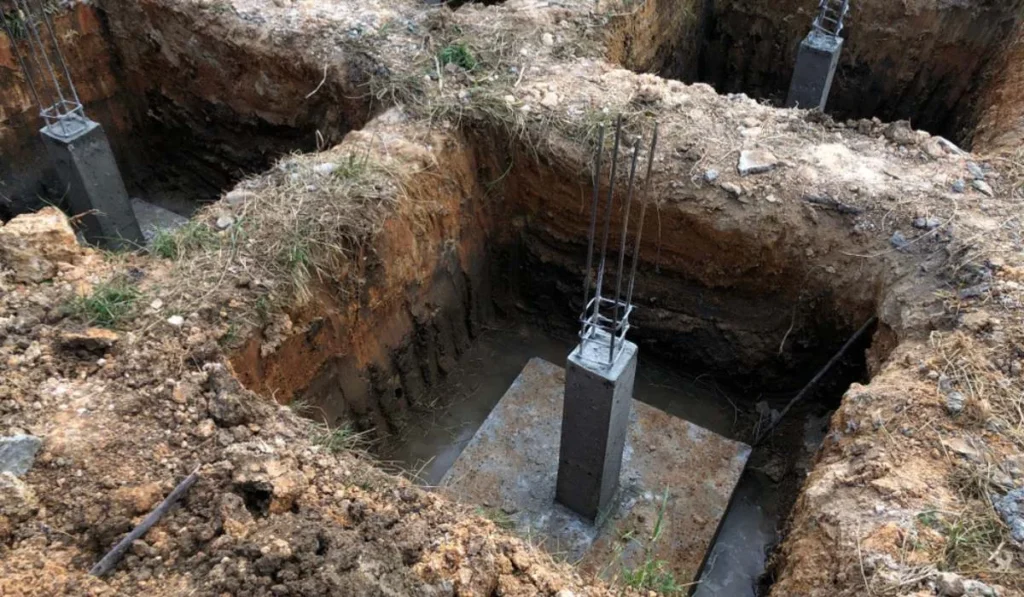

Shallow foundations are types of foundations that transfer building loads to the earth near the surface, rather than to a subsurface layer. They are suitable for buildings with light loads or in areas with strong soil. Shallow foundations are also cost-effective and easy to construct. You can learn more about it here.
a) Spread Footings
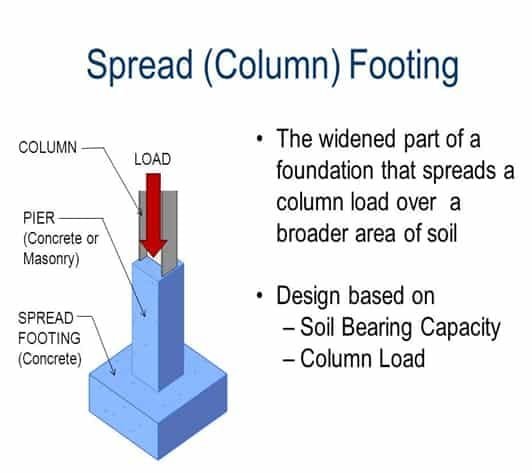
Spread footing is a type of shallow foundation used for single columns or pillars. It is a rectangular or square-shaped foundation that bears the load of the column and transfers it to the soil below. Spread footings are commonly used in residential construction and light commercial buildings.
b) Slab-on-Grade
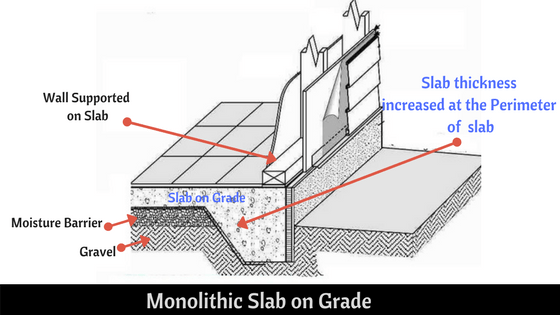
A slab-on-grade foundation is a type of shallow foundation where the concrete slab is poured directly onto the ground. It is commonly used in areas with high water tables or expansive soils. The slab-on-grade foundation is cost-effective and easy to construct. It is commonly used in residential construction and light commercial buildings.
c) Mat Foundations
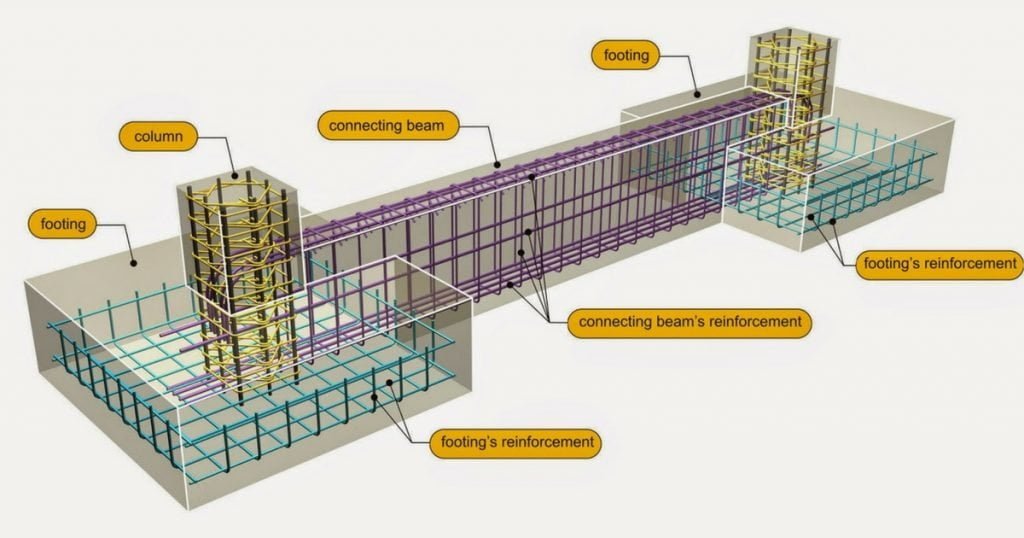
Mat foundations are also known as raft foundations. They are a type of shallow foundation that spreads the load from the building over a large area. The mat foundation is like a raft floating on the soil, hence the name. It is suitable for buildings with heavy loads or in areas with weak soil. Mat foundations are commonly used in high-rise buildings, industrial buildings, and bridges.
In conclusion, shallow foundations are suitable for buildings with light loads or in areas with strong soil. Spread footings, slab-on-grade, and mat foundations are the most common types of shallow foundations used in building construction. The choice of foundation type depends on the building load, soil conditions, and cost.
2. Deep Foundations
Deep foundations are used in construction when the soil near the surface is weak or compressible to support the loads of the structure. They are designed to transfer the building’s load to the deep part of the ground where the soil is strong enough to support it. There are three types of deep foundations that are commonly used in building construction: pile foundations, drilled shafts, and caissons.
a) Pile Foundations

Pile foundations are long, slender, structural elements made of wood, concrete, or steel. They are driven into the ground to transfer the building’s load to the firm soil or rock layer beneath. Piles can be driven vertically or at an angle to provide additional lateral support. They are used in situations where the soil is not strong enough to support the building’s weight or where the building is located in an area prone to earthquakes or other natural disasters.
b) Drilled Shafts
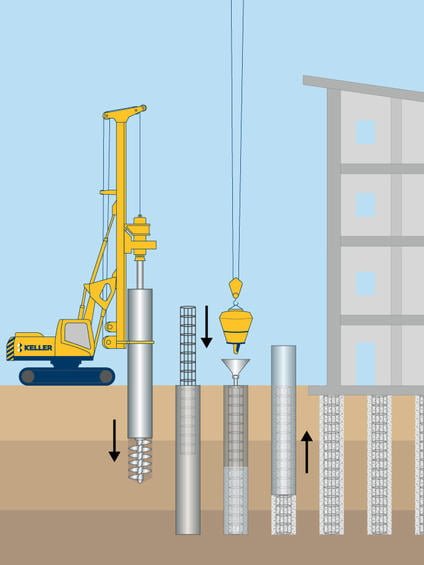

Drilled shafts, also known as bored piles, are cylindrical holes that are drilled into the ground and filled with concrete. They are used to transfer the building’s load to the firm soil or rock layer beneath. Drilled shafts are commonly used in areas where the soil is too weak to support the building’s weight or where the building is located in an area prone to earthquakes or other natural disasters. You can learn about soild strength and the factors that affect it here.
c) Caissons
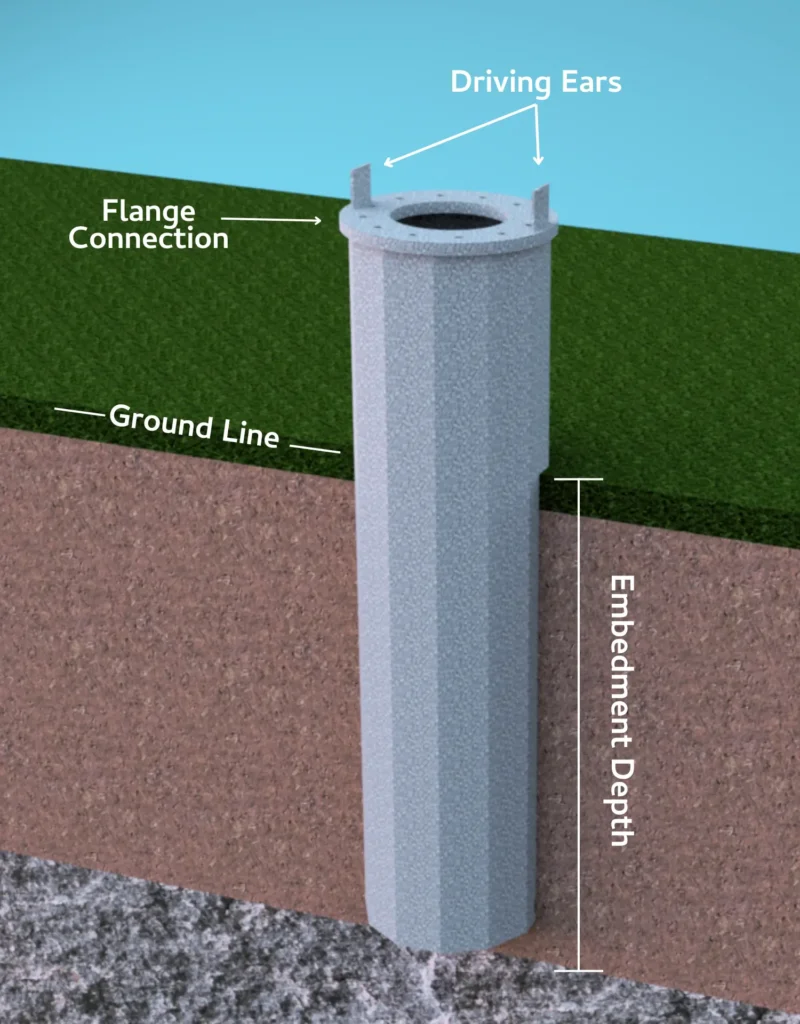
Caissons are large, watertight structures that are sunk into the ground to support the weight of the building. They are typically used in areas where the soil is too weak to support the building’s weight or where the building is located in an area prone to flooding or other natural disasters. Caissons can be open or closed, depending on the soil conditions and the building’s requirements.
Overall, deep foundations are an important part of building construction. They are designed to transfer the building’s load to the deep part of the ground where the soil is strong enough to support it. Pile foundations, drilled shafts, and caissons are the three most common types of deep foundations used in construction.
3. Specialized Foundations
Specialized foundations are used in specific circumstances where the standard foundations are not sufficient. These types of foundations are designed to meet the requirements of the construction site and the building being constructed.
a) Raft Foundations
Raft foundations, also known as mat foundations, are a type of foundation that is used when the soil is weak and cannot support the weight of the building. A raft foundation is a large, flat concrete slab that covers the entire area of the building. The slab is reinforced with steel bars and is supported by beams that are embedded in the soil. Raft foundations are commonly used in areas with poor soil conditions, such as areas with high water tables or soft soil.
b) Pad Foundations

Pad foundations, also known as isolated footings, are used to support individual columns or piers. They are designed to transfer the load of the column or pier to the soil beneath it. Pad foundations are typically square or rectangular in shape and are constructed of reinforced concrete. They are commonly used in residential and small commercial buildings.
c) Strip Foundations

Strip foundations are used to support walls and other structural elements of a building. They are typically used in areas with good soil conditions and are constructed of reinforced concrete. Strip foundations are designed to distribute the load of the building over a wider area of soil. They are commonly used in larger commercial and industrial buildings.
Overall, specialized foundations are an essential part of building construction. They are designed to meet the specific requirements of the building and the construction site, ensuring that the building is safe and stable.
Foundation Materials and Construction
When it comes to constructing a foundation, there are several materials that can be used depending on the soil type, climate, and load-bearing capacity required. The most common materials used in foundation construction include concrete, steel, timber, and masonry. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it is essential to consult with a structural engineer or foundation contractor to determine the best material for the job.
1. Concrete Foundations
Concrete is a popular material for foundation construction due to its durability and strength. It can be poured into any shape and size, making it a versatile option for different types of foundations. Additionally, concrete is resistant to fire, pests, and moisture, making it ideal for areas with extreme weather conditions. However, concrete can be expensive, and its carbon footprint is relatively high.
2. Steel Foundations
Steel foundations are an excellent option for buildings that require a high level of stability and durability. They are ideal for structures that need to withstand high winds, earthquakes, and other natural disasters. Steel foundations are also easy to install, and they are resistant to pests and moisture. However, steel foundations can be expensive, and they require regular maintenance to prevent rust and corrosion.
3. Timber Foundations
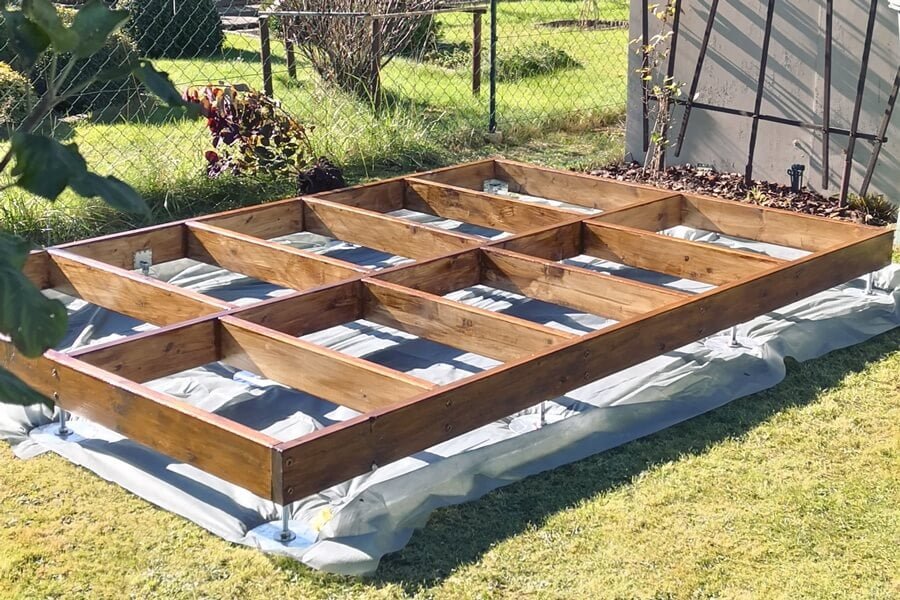

Timber foundations are a popular choice for residential buildings and small structures. They are easy to install and cost-effective, making them an excellent option for those on a tight budget. Additionally, timber is a renewable resource and has a lower carbon footprint than other materials. However, timber foundations are not as durable as other materials and require regular maintenance to prevent rot and decay.
4. Masonry Foundations

Masonry foundations are made of brick, stone, or concrete blocks. They are an excellent option for buildings that require a high level of stability and durability. Masonry foundations are resistant to fire, pests, and moisture, making them ideal for areas with extreme weather conditions. Additionally, masonry foundations are relatively easy to install and require little maintenance. However, masonry foundations can be expensive, and they are not as versatile as other materials.
In conclusion, the choice of material for foundation construction depends on several factors, including soil type, climate, and load-bearing capacity required. Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages, and it is essential to consult with a structural engineer or foundation contractor to determine the best material for the job.
Foundation Design Considerations
1. Soil Analysis and Bearing Cpacity
Before designing a foundation, it is crucial to analyze the soil type and its bearing capacity. Soil analysis helps in determining the type of foundation that is suitable for the structure. The bearing capacity of the soil is the maximum load that the soil can support per unit area without undergoing excessive settlement or shear failure. The foundation design must ensure that the load of the structure is distributed evenly on the soil. The depth of the foundation depends on the soil type and its bearing capacity.
2. Load Distribution
The load distribution is an essential factor to consider in foundation design. The foundation must be designed to distribute the load of the structure evenly on the soil. The design must ensure that the load of the structure is not concentrated on a particular area of the foundation. The foundation design must also consider the dynamic loads that the structure may experience, such as wind loads, seismic loads, and vibration loads.
3. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and chemical exposure can affect the foundation’s stability and durability. The foundation design must consider the environmental factors that the structure may be exposed to. For example, if the structure is in an area with high moisture content, the foundation must be designed to resist the effects of moisture. If the structure is in an area with high chemical exposure, the foundation must be designed to resist the effects of chemicals.
The type of foundation used in construction depends on several factors, including the soil type, bearing capacity, load distribution, and environmental factors. The most common types of foundations used in construction are shallow foundations, deep foundations, and floating foundations. Shallow foundations are suitable for structures with light loads, while deep foundations are suitable for structures with heavy loads. Floating foundations are suitable for structures in areas with a high water table.
In conclusion, the design of the foundation is crucial to the stability and durability of the structure. The foundation design must consider the soil type, bearing capacity, load distribution, and environmental factors. The type of foundation used in construction depends on several factors, including the load of the structure, soil type, bearing capacity, and environmental factors.
Case Studies and Applications
1. Residential Foundations
For residential buildings, the most common type of foundation used is the strip foundation. This type of foundation is suitable for buildings with light loads and is constructed by excavating a strip of soil and pouring concrete into the trench. The foundation is then reinforced with steel bars to strengthen it.
An example of a residential foundation is a single-story house built on a strip foundation. The foundation is designed to support the weight of the house and prevent it from sinking into the ground. The foundation is also designed to withstand the forces of wind and earthquakes.
2. Commercial foundations
For commercial buildings, the type of foundation used depends on the size and weight of the building. The most common types of foundations used for commercial buildings are the raft foundation and the pile foundation.
A raft foundation is a large concrete slab that covers the entire area of the building. The slab is reinforced with steel bars to strengthen it and is designed to distribute the weight of the building evenly across the ground. This type of foundation is suitable for buildings with heavy loads.
A pile foundation is used when the soil is weak and cannot support the weight of the building. Piles are driven into the ground and connected to a concrete foundation. This type of foundation is suitable for tall buildings and structures built on soft soil.
An example of a commercial foundation is a shopping mall built on a raft foundation. The foundation is designed to support the weight of the building and the heavy loads of the stores and customers.
3. Infrastructure Foundations
For infrastructure projects such as bridges, tunnels, and highways, the type of foundation used depends on the location and soil conditions. The most common types of foundations used for infrastructure projects are the pile foundation and the drilled shaft foundation.
A pile foundation is used when the soil is too weak to support the weight of the structure. Piles are driven into the ground and connected to a concrete foundation. This type of foundation is suitable for bridges and highways.
A drilled shaft foundation is used when the soil is too hard to drive piles into. A hole is drilled into the ground and filled with concrete and steel reinforcement. This type of foundation is suitable for tunnels and underground structures.
An example of an infrastructure foundation is a bridge built on a pile foundation. The foundation is designed to support the weight of the bridge and the traffic that crosses it.
In conclusion, the type of foundation used in construction depends on the size and weight of the structure, the soil conditions, and the location of the project. The above case studies and applications provide a basic understanding of the different types of foundations used in residential, commercial, and infrastructure projects.
Blogs you might
find useful
FAQs
What are the main categories of foundations used in building construction?
The main categories of foundations used in building construction are shallow foundations and deep foundations. Shallow foundations include mat foundations, strip foundations, and pad foundations. Deep foundations include pile foundations, drilled shaft foundations, and caisson foundations.
How do shallow foundations differ from deep foundations?
Shallow foundations are typically used for lighter loads and where the soil is relatively stable and strong. They are usually less expensive to construct and can be built more quickly than deep foundations. Deep foundations, on the other hand, are used for heavier loads, where the soil is weak or unstable, and where the groundwater is high. They are typically more expensive to construct and take longer to build.
What factors determine the choice of foundation for a construction project?
Several factors influence the choice of foundation for a construction project. These include the type of soil, the weight of the structure, the size and shape of the structure, the depth of the groundwater table, and the local building codes and regulations.
Can you list the most common materials used in the construction of foundations?
The most common materials used in the construction of foundations include concrete, reinforced concrete, masonry, and steel.
What are the structural differences between mat, strip, and pad foundations?
Mat foundations are large, thick slabs of reinforced concrete that cover the entire area beneath a structure. They are used to distribute the weight of the structure evenly over a large area. Strip foundations are long, narrow concrete footings that support a row of columns or walls. They are used to distribute the weight of the structure evenly along a line. Pad foundations are small, isolated concrete footings that support a single column or wall.
How does soil type influence the selection of foundation in construction?
Soil type is a critical factor in the selection of foundation in construction. The type of soil determines the bearing capacity of the ground and its ability to support the weight of the structure. Different types of soil require different types of foundations. For example, clay soils require deeper foundations than sandy soils, and expansive soils require special foundations that can resist movement caused by changes in moisture content.






